Next-generation ELISA diagnostic assay for Chagas Disease based on the combination of short peptidic epitopes
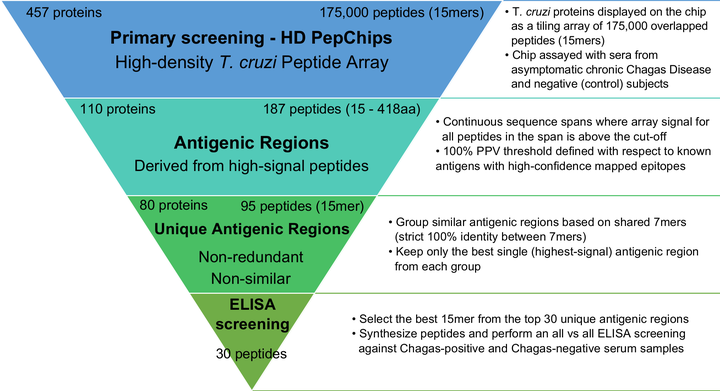 Bioinformatics selection of candidate diagnostic peptides
Bioinformatics selection of candidate diagnostic peptides
Abstract
Chagas disease, caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, is a life-long and debilitating illness of major significance throughout Latin America, and an emergent threat to global public health. Diagnostic tests are key tools to support disease surveillance, and to ultimately help stop transmission of the parasite. However currently available diagnostic methods have several limitations. Identification of novel biomarkers with improved diagnostic characteristics is a main priority. Recently, we conducted a large-scale screening looking for new T. cruzi antigens using short peptides displayed on a solid support at high-density. This led to the identification of several hundred novel antigenic epitopes. In this work we validated the serodiagnostic performance of 27 of these against an extended panel of human serum samples. Based on this analysis, we developed a proof-of-principle multiplex diagnostic kit by combining different validated reactive peptides. Overall, our data support the applicability of high-density peptide microarrays for the rapid identification and mapping epitopes that could be readily translated into novel and useful tools for diagnosis of Chagas disease.